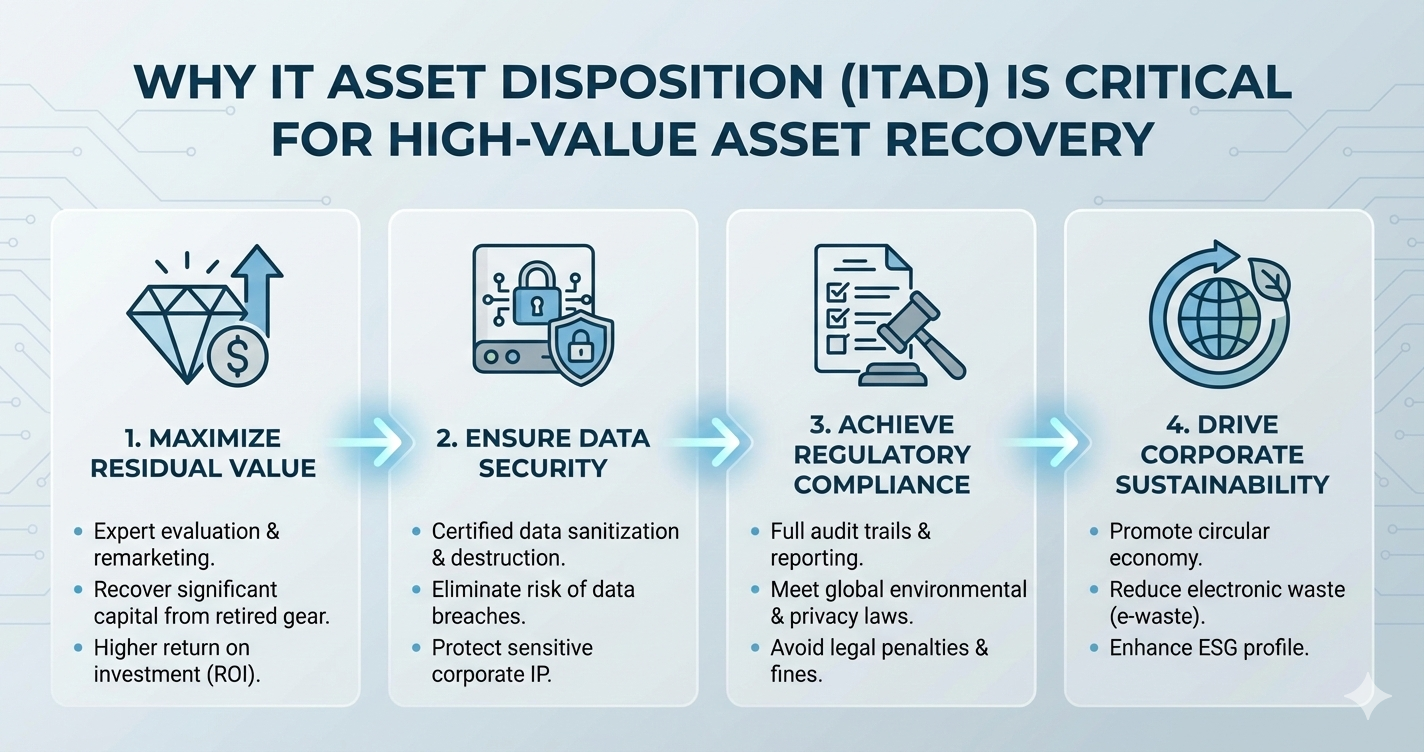
Why Is IT Asset Disposition Critical for High-Value Asset Recovery
As organizations accelerate digital transformation, the lifecycle of IT assets has become shorter and more complex. Servers, laptops, desktops, networking equipment, and data center hardware are constantly being upgraded to support performance, security, and scalability requirements. However, what happens to these assets once they are retired often determines whether a business recovers value or absorbs unnecessary losses.
Many enterprises still treat end-of-life IT equipment as a disposal problem rather than a recovery opportunity. In reality, structured ITAD programs play a critical role in unlocking residual value, ensuring data security, maintaining regulatory compliance, and supporting sustainability goals. When managed strategically, IT asset disposition becomes a powerful lever for high-value asset recovery rather than a cost center.
This blog explores why IT asset disposition is essential for recovering maximum value from retired technology assets, the risks of poor handling, and how professional ITAD services help organizations protect both financial and reputational interests.
Understanding the True Value of Retired IT Assets
IT assets rarely lose all value at the end of their primary use cycle. Even when equipment is no longer suitable for frontline operations, many components retain significant resale, reuse, or refurbishment potential. High-performance servers, enterprise-grade storage devices, and business-class laptops often have extended utility in secondary markets.
Without a structured ITAD approach, organizations risk undervaluing these assets or discarding them prematurely. Devices that could be redeployed internally or remarketed externally may end up sitting idle in storage rooms, losing value with every passing month.
Effective IT asset disposition recognizes that retirement does not mean redundancy. Instead, it marks the transition to the next phase of the asset lifecycle, where recovery and optimization are possible.
The Financial Impact of Inefficient Asset Disposition
High-value IT assets represent a significant investment. When these assets are not managed properly at end of life, organizations experience direct financial losses. These losses occur in multiple ways, including missed resale opportunities, increased storage costs, and unnecessary write-offs.
An unplanned disposal process often leads to bulk scrapping, where valuable equipment is sold at minimal returns. In contrast, a structured ITAD strategy focuses on asset grading, testing, and market alignment to extract the highest possible value.
For large enterprises managing hundreds or thousands of devices, even small improvements in recovery rates can translate into substantial financial gains. This makes IT asset disposition a critical component of financial stewardship and cost optimization.
Data Security as a Core Driver of ITAD Importance
One of the most overlooked risks associated with retired IT assets is data exposure. Hard drives, solid-state storage, and embedded memory often retain sensitive corporate, customer, or employee data long after systems are decommissioned.
Improper disposal can result in data breaches, legal penalties, and reputational damage. Regulatory frameworks increasingly hold organizations accountable for data protection throughout the entire asset lifecycle, including disposal.
Professional ITAD services ensure secure data sanitization through certified wiping, degaussing, or physical destruction processes. This not only protects sensitive information but also allows assets to move safely into resale or reuse channels where appropriate.
By integrating data security into asset recovery, organizations turn a potential liability into a controlled and compliant process.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation
IT asset disposition is closely tied to regulatory compliance. Laws related to data protection, electronic waste management, and environmental responsibility impose strict obligations on organizations handling retired technology.
Failure to comply can result in audits, fines, and long-term brand damage. Informal disposal practices, such as selling equipment to unauthorized vendors or dumping electronic waste, expose businesses to significant legal risk.
A structured ITAD program provides documentation, audit trails, and certifications that demonstrate compliance with applicable regulations. This transparency is especially important for industries such as finance, healthcare, IT services, and government, where compliance standards are stringent.
By treating IT asset disposition as a governance function rather than an afterthought, organizations strengthen their overall risk management framework.
Asset Visibility and Lifecycle Transparency
One of the challenges enterprises face is maintaining visibility over their IT assets once they leave active use. Without proper tracking, organizations lose control over where assets go, how they are handled, and whether value is recovered.
Effective ITAD programs provide end-to-end visibility, from asset identification and collection to final disposition. This transparency enables better decision-making around reuse, resale, or recycling.
Accurate reporting also supports internal audits and helps finance and IT teams align on asset depreciation, recovery value, and lifecycle performance. IT asset disposition thus becomes an extension of asset management rather than a disconnected process.
Maximizing Recovery Through Reuse and Refurbishment
Not all retired IT assets need to be sold externally. Many organizations can extract value through internal reuse or refurbishment. Devices that no longer meet performance standards for core teams may still be suitable for secondary roles, training environments, or temporary projects.
Refurbishment extends asset life while reducing procurement costs and environmental impact. When internal redeployment is not feasible, professionally refurbished equipment can be sold into secondary markets where demand for reliable enterprise-grade hardware remains strong.
A mature ITAD strategy evaluates each asset individually to determine the most value-positive path forward. This approach ensures that recovery efforts are optimized rather than generalized.
Environmental Responsibility and Sustainable Recovery
Sustainability has become a strategic priority for many organizations, driven by regulatory pressure, stakeholder expectations, and corporate responsibility goals. IT asset disposition plays a crucial role in reducing electronic waste and conserving resources.
Unstructured disposal often leads to improper recycling or landfill dumping, contributing to environmental harm. In contrast, responsible ITAD programs emphasize reuse, material recovery, and environmentally compliant recycling.
By extending the life of IT equipment and ensuring responsible end-of-life processing, organizations reduce their carbon footprint and demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices. Asset recovery and environmental responsibility are not mutually exclusive; when managed correctly, they reinforce each other.
The Hidden Costs of Delayed Asset Disposition
Holding onto retired IT assets may seem harmless, but delays in disposition often erode value. Technology depreciates rapidly, and market demand for specific models declines over time. What could have been resold for meaningful returns today may be worth significantly less in six months.
Storage costs, insurance risks, and asset tracking challenges further add to the hidden cost of delay. Additionally, unused assets still carrying data pose ongoing security risks.
Timely IT asset disposition ensures that recovery happens when market conditions are favorable and risks are minimized. Speed and structure are critical to maximizing outcomes.
Forward-thinking organizations align IT asset disposition with broader business objectives such as cost optimization, sustainability, and governance. Rather than treating it as an operational task, they integrate ITAD into strategic planning.
This alignment allows IT, finance, procurement, and sustainability teams to collaborate on asset lifecycle decisions. The result is a cohesive approach where technology investments deliver value not only during use but also at retirement.
When ITAD is embedded into enterprise strategy, high-value asset recovery becomes predictable, measurable, and repeatable.
Why GreenTek Reman Is a Trusted Partner for High-Value IT Asset Recovery
GreenTek Reman brings deep expertise and a sustainability-driven approach to IT asset disposition, helping organizations recover maximum value from retired technology while maintaining the highest standards of security and compliance.
What sets GreenTek Reman apart is its focus on responsible recovery. The company combines secure data sanitization, meticulous asset assessment, and professional refurbishment to ensure that every device is evaluated for its true recovery potential. Assets suitable for reuse or resale are processed to maximize value, while end-of-life equipment is handled through environmentally compliant recycling channels.
GreenTek Reman’s transparent reporting and audit-ready documentation provide clients with complete visibility into the disposition process. This level of accountability supports regulatory compliance, internal governance, and sustainability reporting.
By aligning financial recovery with environmental responsibility, GreenTek Reman helps organizations transform IT asset disposition into a strategic advantage rather than a compliance burden.
Conclusion
In an era where technology investments are substantial and scrutiny around data and sustainability is increasing, IT asset disposition has become a critical function for modern enterprises. When managed strategically, it protects sensitive information, ensures regulatory compliance, and unlocks significant recovery value from retired assets.
Organizations that approach ITAD as an integrated lifecycle process rather than a disposal task are better positioned to reduce risk, improve financial outcomes, and meet sustainability goals. With experienced partners like GreenTek Reman, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of IT asset disposition while turning end-of-life technology into measurable value.