GreenTek Reman: Your Trusted Partner for Eco-Friendly E-Waste Processing Solutions
Electronic garbage, or “e-waste,” has increased drastically in recent years due to the widespread use of electronic gadgets, creating serious environmental problems on a global scale. India is especially impacted by the buildup of e-waste due to its quickly expanding population and economy. In order to discover long-term solutions for this problem, it is essential to comprehend the e-waste processing process and its detrimental effects on the environment.
We will explore the reasons behind the issue of e-waste in India, the recycling process, the harm that e-waste causes to the environment, and how Green Tek Reman is your go-to source for e-waste management solutions.
Why is E-Waste in India a Problem?
95% of e-waste is handled illegally by the informal sector, despite the fact that India has quadrupled its e-waste collection and processing capacity in the last four years. The so-called “kabadiwalas,” or informal rubbish pickers, disregard environmental regulations and burn goods that cannot be recycled or sent to landfills, which might have a serious negative impact on the environment and pose health risks.
Moreover, informal sector recyclers employ crude recycling methods that might discharge harmful contaminants into the environment. The environment and human health are seriously endangered by many of the harmful compounds found in e-waste.
With an annual production of 3.23 million tonnes, India ranks third in the world’s e-waste production after the United States and China. India handled 3.4 lakh tonnes of e-waste in 2020–2021. The CPCB reports that the amount of plastic garbage generated annually is rising by 3%. The amount of e-waste generated is even higher, amounting to 7.1 lakh tonnes in 2018–19 and 10.14 lakh tonnes in 2019–20. There is an annual growth of 31%.
In 22 states, there are just 468 authorized recyclers and 2,808 pickup locations. The 13 lakh tonnes of capacity held by 468 recyclers is not enough to meet the country of India’s e-waste generating needs.
Understanding the E-Waste Processing
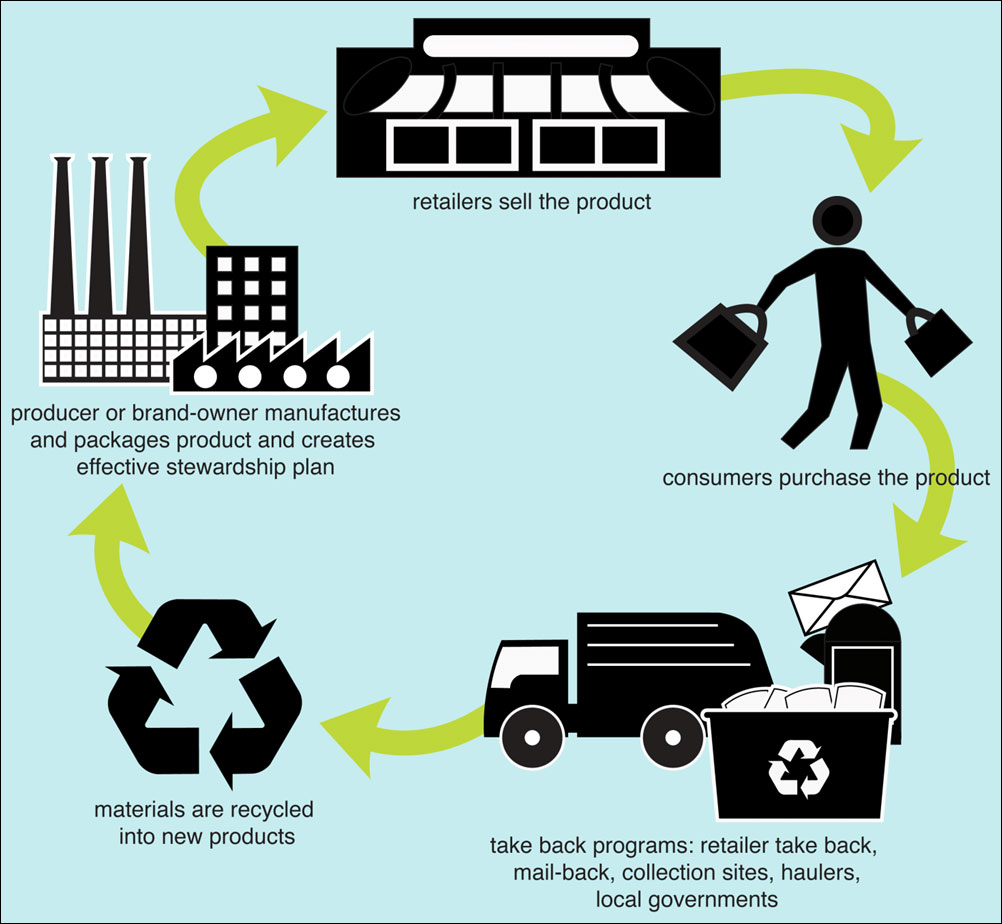
E-waste processing entails a number of procedures designed to break down electronic gadgets, separate their parts, and recycle materials so they can be used again. The e-waste procedure usually starts with gathering e-waste from multiple sources, then classifying and arranging the devices according to their kind and parts. The gadgets are then disassembled, and the glass, plastic, and metal parts are segregated for recycling. Melting and shredding are two examples of advanced technologies used to effectively recover precious components from e-waste.
What are the Negative Effects on the Environment?
The environment is being negatively impacted in numerous ways:
- India has a serious problem with air pollution; the country is home to nine of the 10 most polluted cities worldwide
Burning plastic and other low-value e-waste releases small particles into the atmosphere. When done incorrectly, the process of desoldering, which extracts gold and silver from e-waste materials, can release hazardous vapors and toxins.
- 80 % of India’s surface water is contaminated, with the holy rivers Yamuna and Ganga ranked among the world’s most polluted
Because hazardous chemicals seep into surface water from landfills, disposing of e-waste in landfills has an effect on both surface and groundwater.
Toxic residues from incorrect e-waste recycling will also wind up in city drains and sewers. If these products get into nearby waterways, they can contaminate the surface water.
How is E-Waste in India Recycled?
Recycling e-waste presents a challenge because discarded electronic equipment are complex gadgets made of different ratios of metal, plastic, and glass. The material and technique used determine the differences in the recycling process.
- Collection and transportation
In any recycling process, including the recycling of e-waste, collection and transportation are the first steps. Recyclers transfer the waste gathered to recycling facilities or centers by placing collecting bins or electronics take-back booths in strategic locations.
- Shredding, Sorting, and Separation
- To make new products, the gathered material will be processed and divided into clean commodities.
- Sorting and separating plastic from metals and internal circuitry is the first step in the shredding of electronic debris. Before being sorted, e-waste is shredded into 100mm pieces.
- On the conveyor, steel and iron are separated from waste streams by a powerful magnet.
- The material stream is currently primarily composed of plastic, and aluminum, copper, and circuit boards are separated from it via mechanical processing. Water separation technology is used to remove glass from polymers.
- Visual inspection and manual sorting help to improve the quality of the retrieved materials.
- Finding and removing any leftover traces of metal from the plastics is the last stage in the separation process that further purifies the stream.
- After the shredding, sorting, and separating processes are finished, the separated materials can be purchased as usable raw materials to be used in the production of new electronics or other items.
Also Read : Revolutionize Sustainability With E-Waste Recycling Companies in Delhi
Green Tek Reman: The Reliable Source for all your Recycling E-Waste Management
For environmentally responsible recycling e-waste management solutions in India, Green Tek Reman is your go-to partner. With a team of professionals and cutting-edge facilities, we provide dependable and effective e-waste management services that are customized to your requirements. Our all-encompassing strategy for recycling e-waste guarantees that electronic gadgets are treated carefully and disposed of appropriately, reducing their negative effects on the environment and public health. You can be confident that your e-waste will be managed effectively and sustainably by working with Green Tek Reman, helping to create a cleaner and greener future for India and beyond.