IT Asset Disposition Explained: A Complete Guide for Enterprises
As enterprises accelerate digital transformation, IT infrastructure is constantly evolving. New hardware is deployed, systems are upgraded, and outdated devices are retired at a faster pace than ever before. While much attention is given to procurement and deployment, the final stage of the IT lifecycle is often overlooked. This stage, known as IT asset disposition, plays a critical role in security, compliance, cost recovery, and sustainability.
Improper handling of retired IT assets can expose enterprises to data breaches, regulatory penalties, and reputational risks. On the other hand, a well-structured disposition strategy helps organizations recover value, protect sensitive information, and support environmental responsibility.
This guide explains ITAD in detail, covering its importance, processes, risks, best practices, and how enterprises can implement a secure and compliant approach.
Understanding IT Asset Disposition in the Enterprise Context
IT asset disposition refers to the structured process of managing, retiring, and disposing of IT equipment that is no longer required by an organization. This includes servers, desktops, laptops, storage devices, networking equipment, and other enterprise hardware.
In large organizations, IT assets are deployed across multiple locations, departments, and environments. Over time, these assets reach end-of-life due to performance limitations, hardware failures, technology upgrades, or changes in business requirements.
A formal disposition strategy ensures that these assets are handled responsibly from both a data security and environmental standpoint, rather than being discarded without proper controls.
Enterprises handle vast amounts of sensitive data, including customer information, financial records, intellectual property, and internal communications. When IT equipment is retired, residual data often remains on storage devices if not properly erased.
Without a secure disposition process, organizations risk data leaks that can result in financial losses and legal consequences. Regulatory frameworks across industries increasingly mandate secure data handling even after assets are decommissioned.
Beyond compliance, enterprises also face growing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. Responsible disposition helps reduce electronic waste and supports corporate environmental goals.
Key Components of an Effective ITAD Process
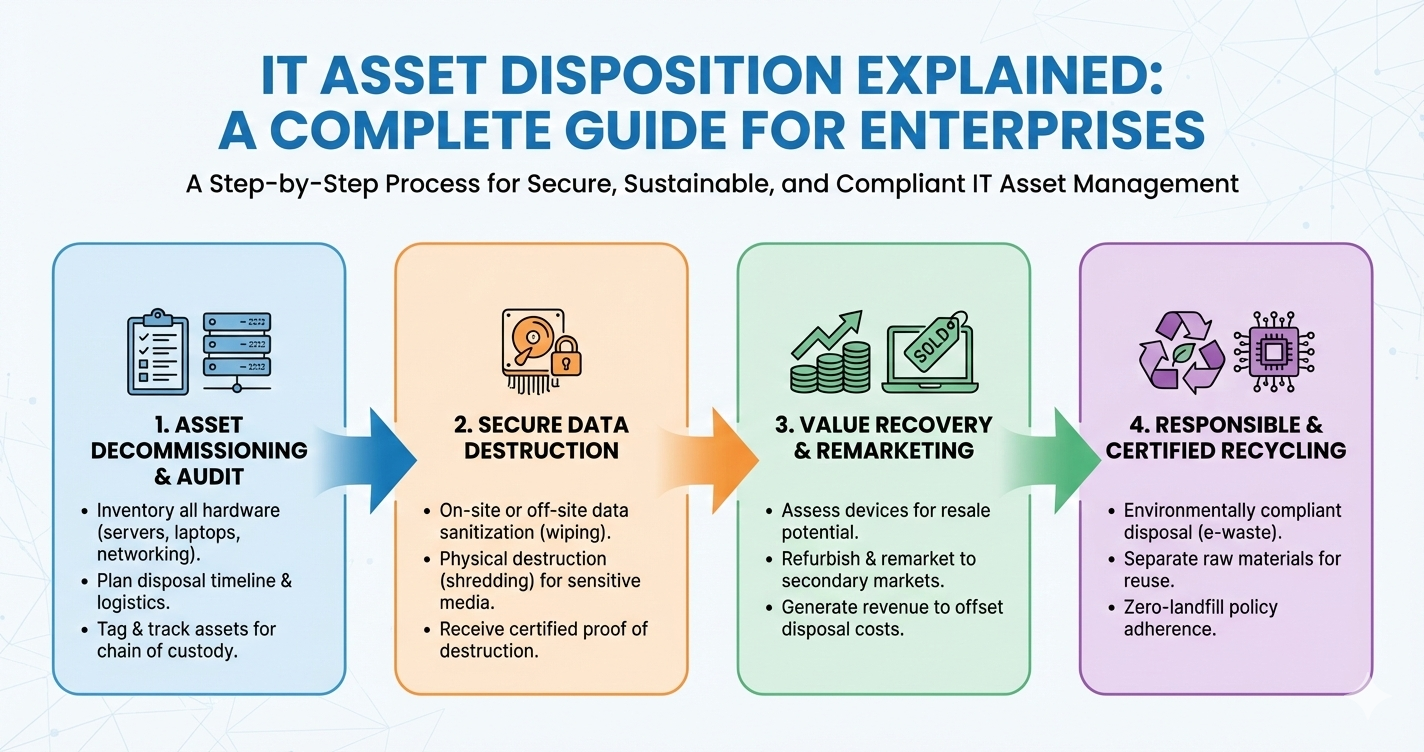
A successful IT asset disposition program involves multiple interconnected steps that ensure security, accountability, and value recovery. The process begins with asset identification and inventory validation. Enterprises must know exactly which assets are being retired, their configurations, and their data sensitivity level.
Next comes data sanitization, where all data is securely erased using industry-approved methods. This step is essential to prevent unauthorized access to residual data. After data removal, assets are evaluated for reuse, resale, refurbishment, recycling, or destruction. Each option is chosen based on the condition of the asset, compliance requirements, and sustainability goals.
Finally, documentation and reporting are completed to provide audit trails and proof of compliance.
Data Security Risks Associated With Improper Disposal
One of the most significant risks in IT asset disposition is data exposure. Storage devices such as hard drives and solid-state drives retain data even after files are deleted or systems are reformatted.
If assets are sold, donated, or recycled without secure data erasure, sensitive information can be recovered using readily available tools. This creates serious risks, particularly for enterprises operating in regulated sectors.
A structured disposition strategy includes certified data destruction or erasure processes, ensuring that no recoverable data remains on retired assets.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Enterprises must comply with various data protection and environmental regulations depending on their industry and geography. These regulations often extend to how retired IT assets are handled.
Failure to follow proper disposition practices can result in penalties, audits, and loss of trust. Maintaining detailed records of asset disposition activities helps organizations demonstrate compliance during audits. Working with experienced disposition partners ensures that regulatory requirements are met consistently across all locations.
Environmental Impact of IT Asset Disposal
Electronic waste is one of the fastest-growing waste streams globally. Improper disposal of IT equipment contributes to pollution, resource depletion, and health hazards.
Enterprises are increasingly expected to adopt environmentally responsible practices throughout the IT lifecycle. Responsible disposition focuses on reuse, refurbishment, and recycling to minimize landfill waste.
By extending the usable life of IT assets through remanufacturing and resale, organizations can significantly reduce their environmental footprint. An effective ITAD strategy includes assessing assets for resale or redeployment. Value recovery helps offset the cost of new hardware investments and improves overall return on IT spend.
Enterprises that integrate value recovery into their disposition planning often achieve better financial outcomes while supporting sustainability goals.
Challenges Enterprises Face in IT Asset Disposition
Managing IT asset disposition at an enterprise scale is complex. Organizations often struggle with decentralized asset ownership, inconsistent processes, and lack of visibility into asset lifecycles.
Logistics is another challenge, especially for enterprises with multiple offices or data centers. Secure transportation and tracking of retired assets require coordination and expertise.
Additionally, internal IT teams may lack the specialized tools and certifications needed for secure data destruction and compliant recycling, increasing the risk of errors.
Best Practices for Enterprise ITAD Programs
Due to the complexity and risks involved, many enterprises rely on specialized service providers to manage IT asset disposition. These providers bring expertise, infrastructure, and standardized processes that internal teams may not have.
A professional ITAD partner handles data sanitization, asset testing, refurbishment, recycling, and compliance reporting under a single framework. This reduces operational burden and ensures consistency across locations.
Choosing the right partner is essential to achieving security, compliance, and value recovery objectives. Enterprises can strengthen their disposition strategy by adopting a few best practices.
Creating a formal policy ensures that asset retirement follows consistent procedures across departments. Clear documentation helps reduce ambiguity and improves accountability.
Integrating disposition planning into the broader IT lifecycle allows organizations to plan ahead rather than reacting when assets reach end-of-life. Regular audits and reviews help identify gaps and improve processes over time. Training internal teams on disposition protocols further reduces risk.
Many enterprises now include sustainability as a core business objective. IT asset disposition plays an important role in achieving these goals. By prioritizing reuse and refurbishment, organizations reduce demand for new manufacturing and lower carbon emissions. Responsible recycling ensures hazardous materials are handled safely.
Transparent reporting on disposition outcomes also supports sustainability disclosures and strengthens corporate credibility.
How Greentek Reman Adds Value to Enterprise IT Asset Disposition
Greentek Reman plays a strategic role in helping enterprises manage IT asset disposition with confidence and clarity. The company specializes in responsible remanufacturing, refurbishment, and recycling of IT assets, ensuring that retired equipment is handled securely and sustainably.
What differentiates Greentek Reman is its strong focus on data security, environmental responsibility, and value recovery. Every asset undergoes structured data sanitization processes aligned with industry standards, minimizing the risk of data exposure.
Greentek Reman’s remanufacturing capabilities allow enterprises to recover maximum value from retired assets while supporting circular economy principles. By extending the usable life of IT equipment, the company helps organizations reduce electronic waste and meet sustainability objectives.
With transparent reporting, traceability, and compliance-driven processes, Greentek Reman enables enterprises to transform IT asset disposition from a risk-prone activity into a strategic advantage.
Conclusion
A structured and well-managed approach to ITAD helps organizations protect sensitive information, recover value from retired assets, and reduce environmental impact. As regulatory scrutiny and sustainability expectations continue to grow, enterprises cannot afford to treat asset disposal as an afterthought.
By partnering with experienced and responsible providers such as GreentekReman, enterprises can ensure that their IT assets are retired securely, compliantly, and sustainably. A strong disposition strategy not only mitigates risk but also supports long-term business resilience and responsible growth.